Quick links:
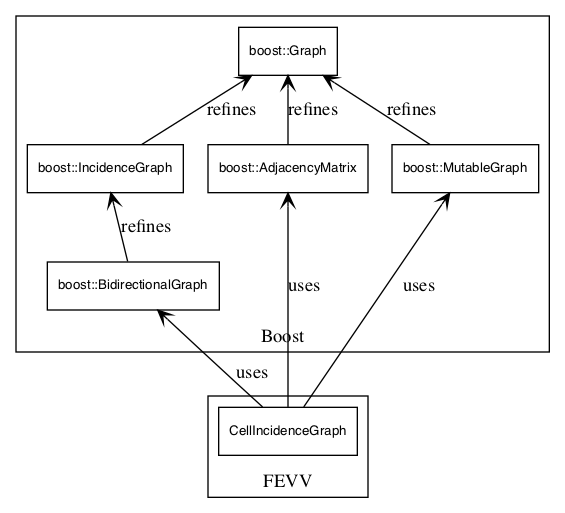
Diagram reference: boost::Graph concepts diagram
Introduction
The objective of the CellIncidenceGraph concept is to refine the graph notion when representing the incidence relationships of cell-meshes. CellIncidenceGraph enables the representation of the topological aspects of cell-meshes i.e. they allow the capture the topology of e.g.
- non manifold surface meshes
- volumic cell-mesh
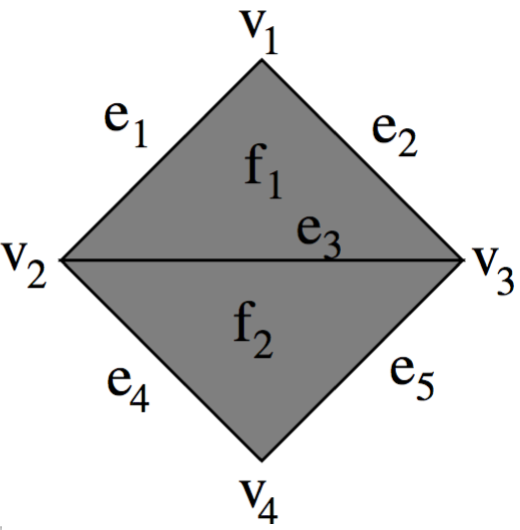
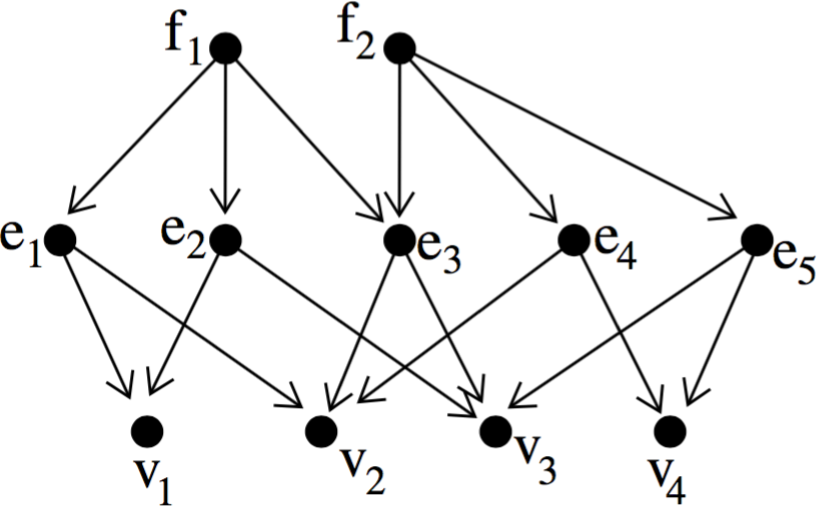
In order to clearly understand the relationship between a given cell-mesh and the CellIncidenceGraph that captures its topology, one must first distinguish the two structures. One simple way to do so, is to use different terminologies for both concepts and in particular to distinguish:
- the CellIncidenceGraph nodes that can refer to
- mesh vertices: mesh cells with dimension
0, - mesh edges: mesh cells with dimension
1, - mesh faces: mesh cells with dimension
2, - volumic cells...
- mesh vertices: mesh cells with dimension
- the CellIncidenceGraph edges from the incidence relations between mesh cells
A CellIncidenceGraph node has no dimension per se (its a topological concept). Yet a node corresponds to (or refers to) a mesh-cell that has a dimension (e.g. 2 for face). By abuse of language one can speak of a CellIncidenceGraph node dimension in order to refer to the dimension of the mesh-cell associated to the considered node.
CellIncidenceGraph edges describe the incidence relationship between a node of some dimension to a node of (immediately) lower dimension. A CellIncidenceGraph is thus an oriented graph that draws its orientation out of the hierarchy of dimensions of the cell-mesh of which it captures the incidence relationship. This enables to partition the edges of node of a CellIncidenceGraph since when given any graph node one can separate:
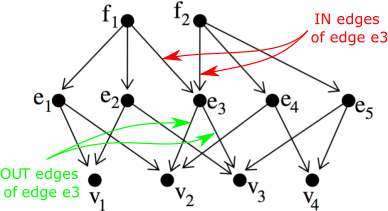
- the node's out edges i.e. the CellIncidenceGraph edges starting from the given node and ending on a node corresponding to a mesh-cell of immediately lower dimension (than the dimension of the mesh cell corresponding to the given node),
- the node's in edges i.e. all the CellIncidenceGraph edges starting from a node corresponding to mesh-cell of immediately upper dimension and ending at the considered node.
Refines
- IncidenceGraph
- see also boost graph concepts and Graph (Boost)
- PropertyGraph (Boost)
Notations
GA type that is a model ofCellIncidenceGraph.gAn object of typeG.u,vVertex descriptors (for nodes ofg).eAn edge descriptor.dA dimension (of an associated cell-mesh)
Associated types
| Type | Reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
cell_iterator | FIXME | Required by cells(d, g): what is this type, where does it come from ? |
size_type | FIXME | Required by num_nodes(d, g): what is this type, where does it come from ? |
edge_iterator | FIXME | Required by remove_edge(iter, g): comes from boost Graph mutability that doesn't define it... |
boost::graph_traits<G>::vertex_descriptor | Graph (boost) | A vertex descriptor corresponds to a unique node in a graph instance. A vertex descriptor must be Default Constructible, Assignable, and Equality Comparable. |
boost::graph_traits<G>::edge_descriptor | Graph (boost) | An edge descriptor corresponds to a unique edge (u,v) in a graph. An edge descriptor must be Default Constructible, Assignable, and Equality Comparable. |
Valid expressions
| Expression | Reference | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BidirectionalGraph (boost) basics | |||
edge(u, v, g) | AdjacencyMatrix (boost) | std::pair<edge_descriptor, bool> | Returns a pair consisting of a flag saying whether there exists an edge between u and v nodes in graph g, and consisting of the edge descriptor if the edge was found. |
source(e,g) | IncidenceGraph (boost) | vertex_descriptor | Returns the node descriptor for node u of the edge (u,v) represented by e. |
target(e,g) | IncidenceGraph (boost) | vertex_descriptor | Returns the node descriptor for node v of the edge (u,v) represented by e. |
out_edges(u, g) | IncidenceGraph (boost) | std::pair<out_edge_iterator, out_edge_iterator> | Returns an iterator-range providing access to the incident edges of node u in graph g. |
out_degree(u, g) | IncidenceGraph (boost) | degree_size_type | Returns the number of out-edges of node u in graph g. |
in_edges(u, g) | BiDirectoinalGraph (boost) | std::pair<in_edge_iterator, in_edge_iterator> | Returns an iterator-range providing access to the in-edges (CellIncidenceGraph being a directed graph) of node u in graph g. The target of an out-edge is required to be vertex u and the source is required to be a vertex that is adjacent to u. |
in_degree(u, g) | BiDirectoinalGraph (boost) | degree_size_type | Returns the number of in-edges of node u in graph g. |
degree(u,g) | BidirectionalGraph (boost) | degree_size_type | Returns the number of incident edges of node u in graph g. |
| Global traversals | |||
dimension(u, g) | FIXME | unsigned int | Returns the dimension of the mesh cell associated with node u in graph g. |
cells(d, g) | FIXME | std::pair<cell_iterator, cell_iterator> | Returns an iterator-range providing access to all the cells of dimension d associated to the nodes of graph g. |
num_nodes(d, g) | FIXME | size_type | Returns the number of nodes associated to a cell of dimension d in graph g. |
| Mutability | MutableGraph (boost) | ||
add_edge(u, v, g) | MutableGraph (boost) | std::pair<edge_descriptor, bool> | Inserts the edge (u,v) into the graph, and returns an edge descriptor pointing to the new edge. When the edge (u,v) is already present in the graph, then the bool flag returned is false. Note that parallel edges are not allowed. |
remove_edge(u,v ,g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove the edge (u,v) from the graph. If the graph were to allow parallel edges then this would remove all occurrences of (u,v). |
remove_edge(e, g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove the edge e from the graph g. |
remove_edge(iter, g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove the edge pointed to by iter from the graph g. Precondition: *iter is an edge in the graph. Postcondition: *iter is no longer in the edge set for g. |
remove_edge_if(p, g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove all edges of graph g for which the predicate p returns true. |
add_vertex(g) | MutableGraph (boost) | vertex_descriptor | Add a new node to the graph. The vertex_descriptor for the new node is returned. |
clear_vertex(u, g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove all edges to and from node u from the graph. |
remove_vertex(v,g) | MutableGraph (boost) | void | Remove u from the node set of the graph. Note that undefined behavior may result if there are edges remaining in the graph who's target is u. Typically the clear_vertex() function should be called first. |
| Miscelaneous | |||
boost::graph_traits<G>::null_vertex() | Graph (boost) | Returns a special boost::graph_traits<G>::vertex_descriptor object which does not refer to any node of graph object which type is G. |
Design notes:
- CellIncidenceGraph differs from IncidenceGraph (boost) in two ways:
- CellIncidenceGraph associates a dimension to its nodes whereas IncidenceGraph doesn't,
- CellIncidenceGraph enforces the following constraint: when the dimension of the source of one of its edge is
ithen the dimension of the target of this edge has to bei-1.
- CellIncidenceGraph do not allow for the representation of parallel edges. As such a CellIncidenceGraph can neither capture the topology of mesh-edge being twice adjacent to the same mesh-vertex nor capture the topology of (mesh) face being twice adjacent to the same mesh-edge (to represent e.g. a topological sphere with two vertices and a single edge adjacent to those two vertices).
- Strictly speaking, the dimension notion used within CellIncidenceGraph is a notion that is not intrisic to the CellIncidenceGraph. In practice a CellIncidenceGraph will always be "extrated" from (or will represent the topology of) a cell-mesh wich is immersed in an ambiant space. The dimension of a CellIncidenceGraph is thus pulled back out of the concrete ambiant space of the cell-mesh (whose geometry is accessed through a Geometry Traits). The dimension type should thus also be pulled from the corresponding Geometry Traits and flown to CellIncidenceGraph (there should be a concrete dependency). For the current implementation of the CellIncidenceGraph concept, the concrete type of
dimensionwill nevetheless be hardwired within CellIncidenceGraph as being anunsigned int. Independently from flowing the type from its conceptual source, we also set aside the naming of the dimension type with a specific type name (e.g. boost geometry defines adimension_size_type) and simply hardwireunsigned int.